Activity 1: Recite the Story Information
- Before and after reading or listening to the story, recite aloud the title and author of the play.
Activity 2: Narrate the Story
- After reading or listening to the story, narrate the events aloud in your own words.
Activity 3: See the Playwright and Poet William Shakespeare
- Study the controversial 'Cobbe portrait' below, which may be a real-life portrait of Shakespeare.
- The portrait contains the Latin phrase 'Principum amicitias!' which means 'The alliances of princes!'
Activity 4: Map the Play
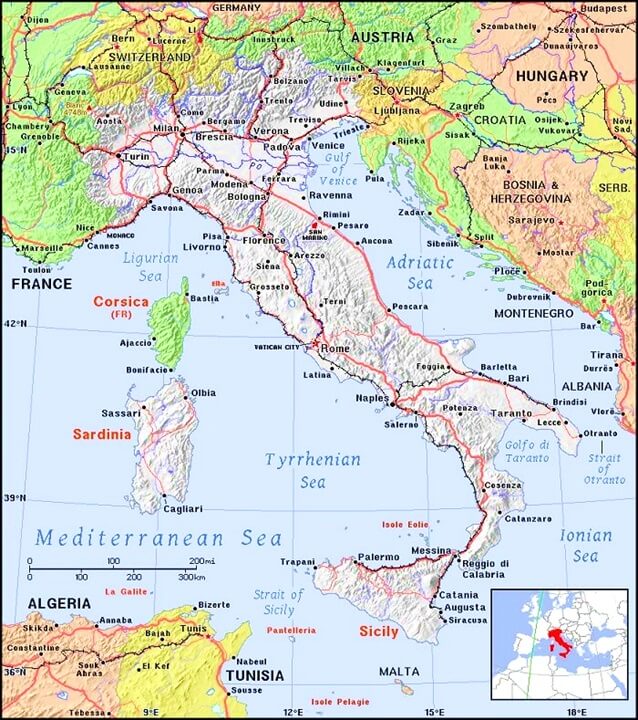
- AEgeon and AEmilia are from Syracuse (Siracusa) on the island of Sicily, Italy.
- Find Siracusa and the Adriatic Sea on the map of Italy.
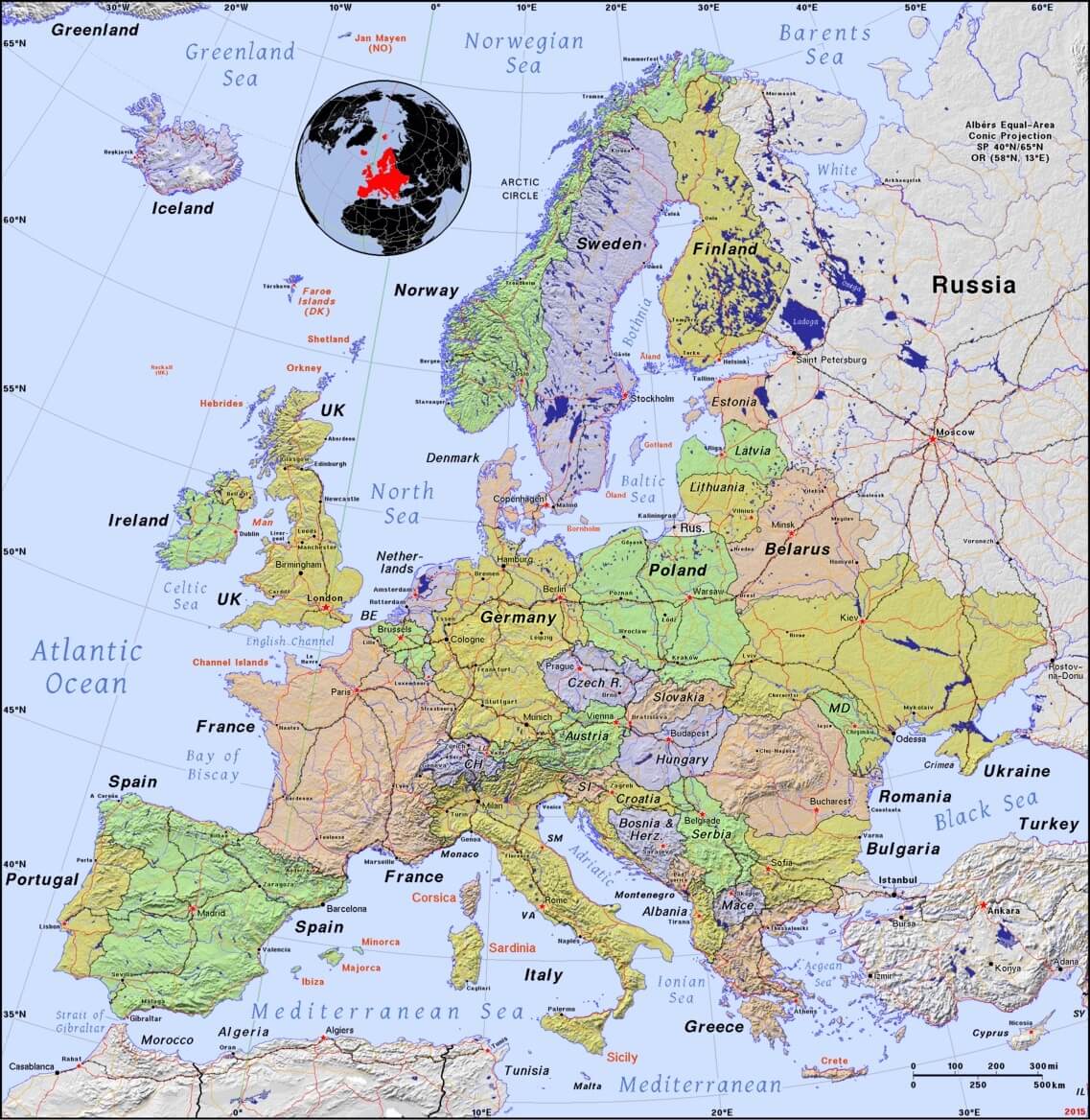
- Find the western shores of present-day Turkey, where the ancient city of Ephesus was once located.
- Point to the locations of Italy and Turkey on the map of the world.
Activity 5: Can You Find It?
During the week, zoom in to study the painting, 'Antipholus of Ephesus, an Officer, and Dromio of Ephesus,' from 'The Comedy of Errors', Act IV, Scene I by J. Coghlan. Find the following:
- Antipholus of Ephesus
- Dromio of Ephesus
- Officer
- Someone Accused of Stealing a Gold Chain
- Pike
- Hat with a Feather
- Capes
- Hosen (leg coverings)
Activity 6: Build the Sets

- Color, cut out, and laminate the set items on page 100 of 'Third Grade Shakespeare Theater Pages.'
- Set up the scenes in your theater.
Activity 7: Study the Order of Events

- Print and cut out Group A of events on page 101 of 'Third Grade Shakespeare Theater Pages.'
- Using what you know from reading the story, arrange the events in the correct order.
- Glue the group of ordered events to a piece of construction paper.
- Repeat for groups B-E on pages 102-105 of 'Third Grade Shakespeare Theater Pages.'
- Keep these event orderings for the next activity.
Activity 8: Act Out the Events
- Use the event orderings from the prior activity, the theater, the laminated characters, and the sets, to act out each group of events.
- The instructor reads aloud events from group A.
- Children build the appropriate set, add necessary characters, and act out the event, moving the characters and inventing their own dialog.
- Repeat for groups B-E.
Activity 9: Contrast Portrayals of the Upper Class versus the Lower Class/Slaves
- Discuss the differences in how the Dromio twins and the Antipholus twins are given happy endings by Shakespeare.
- Discuss the differences in how the Dromio twins and the Antipholus twins are portrayed in the pictures and paintings we've studied.
 Beautiful Stories from Shakespeare I
Stories from Shakespeare I
Beautiful Stories from Shakespeare I
Stories from Shakespeare I




 Beautiful Stories from Shakespeare I
Stories from Shakespeare I
Beautiful Stories from Shakespeare I
Stories from Shakespeare I